Securing the Future: AI Security with the Microsoft Security Stack
Leveraging Microsoft’s Security Tools for Robust AI Protection
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming industries, but its rapid adoption has introduced new security challenges. From adversarial attacks to prompt injections, securing AI systems requires a robust, multi-layered approach. The Microsoft Security Stack provides a comprehensive suite of tools and services to protect AI applications, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability. This blog explores AI security, delves into the Microsoft Security Stack, provides a real-world use case, and illustrates how to leverage AI security with an architectural diagram.
Understanding AI Security Challenges
AI systems, particularly those built on Large Language Models (LLMs), face unique threats:
Adversarial Attacks: Malicious inputs designed to deceive AI models, leading to incorrect outputs or biased decisions.
Prompt Injections: Attackers manipulate prompts to trick AI into performing harmful actions, such as leaking sensitive data.
Model Poisoning: Training data is tampered with to degrade model performance or introduce biases.
Denial of Service (DoS): Overloading AI systems with excessive requests to disrupt service.
Data Privacy Risks: Unauthorized access to sensitive training data or user inputs, risking compliance violations.
These threats demand a security-first approach, integrating protections across the AI stack—from infrastructure to application layers. The Microsoft Security Stack is designed to address these challenges with a Zero Trust framework, advanced threat detection, and governance capabilities.
The Microsoft Security Stack for AI
The Microsoft Security Stack is a comprehensive set of tools and services that integrate seamlessly with AI workloads, providing end-to-end security for hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Key components include:
Microsoft Defender for Cloud: A unified infrastructure security management system that strengthens the security posture of data centers and cloud workloads, including AI platforms.
Microsoft Entra ID: Provides identity and access management, ensuring only authorized users and systems access AI resources.
Microsoft Sentinel: A cloud-native Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solution that uses AI to detect and respond to threats in real time.
Microsoft Security Copilot: An AI-powered tool that enhances security operations by accelerating incident response and threat hunting.
Azure AI Services: Offers secure, prebuilt APIs and models for AI development, with built-in safety systems to filter harmful inputs and outputs.
Microsoft Responsible AI Standard: Ensures ethical AI deployment with governance frameworks for fairness, privacy, and compliance.
These tools align with Microsoft’s Cybersecurity Reference Architectures (MCRA), which emphasize Zero Trust principles to secure AI across legacy IT, multi-cloud, and IoT environments.
Real-World Use Case: Securing a RAG-Based Customer Support Chatbot
Scenario
A global e-commerce company deploys a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) chatbot powered by Azure AI Services to handle customer inquiries. The chatbot retrieves product information from a vector database and generates responses using an LLM like OpenAI’s GPT model hosted on Azure. The company faces risks such as prompt injections, data leaks, and DoS attacks, which could disrupt operations and erode customer trust.
Solution with Microsoft Security Stack
Identity and Access Management with Microsoft Entra ID:
The chatbot is integrated with Microsoft Entra ID to enforce role-based access control (RBAC). Only authorized customer service agents and systems can interact with the chatbot’s backend.
Conditional Access policies ensure that access is granted only from trusted devices and locations, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Threat Detection with Microsoft Sentinel:
Microsoft Sentinel monitors the chatbot’s API endpoints for suspicious activity, such as repeated failed login attempts or unusual query patterns indicative of DoS attacks.
KQL (Kusto Query Language) queries are used to detect prompt injection attempts, such as inputs attempting to override system prompts. For example, a KQL query might flag inputs containing keywords like “ignore previous instructions.”
Infrastructure Security with Microsoft Defender for Cloud:
Defender for Cloud scans the Azure infrastructure hosting the chatbot for vulnerabilities, such as misconfigured storage accounts or outdated dependencies.
It provides real-time alerts for anomalous traffic patterns, helping mitigate DoS attacks through auto-scaling recommendations.
Input/Output Filtering with Azure AI Safety Systems:
Azure AI Services include built-in safety filters to block harmful inputs (e.g., malicious prompts) and outputs (e.g., sensitive data leaks). For instance, the system is configured to reject prompts attempting to extract internal system prompts.
The chatbot’s system prompt is designed to limit responses to product-related queries, reducing the risk of off-topic or harmful outputs.
Governance and Compliance:
The Microsoft Responsible AI Standard ensures the chatbot adheres to ethical guidelines, such as GDPR and HIPAA, by anonymizing user data and logging interactions for auditability.
Microsoft Security Copilot automates compliance reporting, identifying potential biases in the chatbot’s responses and suggesting mitigations.
Outcome
The company successfully deploys a secure RAG chatbot that handles millions of customer queries monthly. Prompt injection attempts are reduced by 95% through input validation, and DoS attacks are mitigated through auto-scaling and Sentinel’s real-time monitoring. Customer trust is maintained, and compliance with data protection regulations is ensured.
The AI Stack and Security Integration
The AI stack comprises layers that work together to deliver intelligent applications. Below is a typical AI stack with examples of how Microsoft Security tools enhance each layer:
Infrastructure Layer:
Components: Compute (e.g., Azure GPUs), storage (e.g., Azure Blob Storage), and networking.
Security: Microsoft Defender for Cloud secures compute resources by monitoring for vulnerabilities and ensuring secure configurations. Azure DDoS Protection mitigates infrastructure-level DoS attacks.
Model Layer:
Components: LLMs (e.g., GPT models via Azure AI Foundry), training frameworks (e.g., PyTorch, TensorFlow).
Security: Azure AI Services filter malicious inputs and outputs, preventing adversarial attacks. Microsoft Entra ID secures access to model APIs.
Application Layer:
Components: User interfaces, APIs, and orchestration (e.g., Azure AI agent orchestration patterns).
Security: Microsoft Sentinel monitors application logs for suspicious behavior, while Microsoft Security Copilot accelerates incident response.
Governance Layer:
Components: Policies for data usage, compliance frameworks (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Security: The Microsoft Responsible AI Standard enforces ethical guidelines, and Microsoft Entra ID Governance ensures proper access controls.
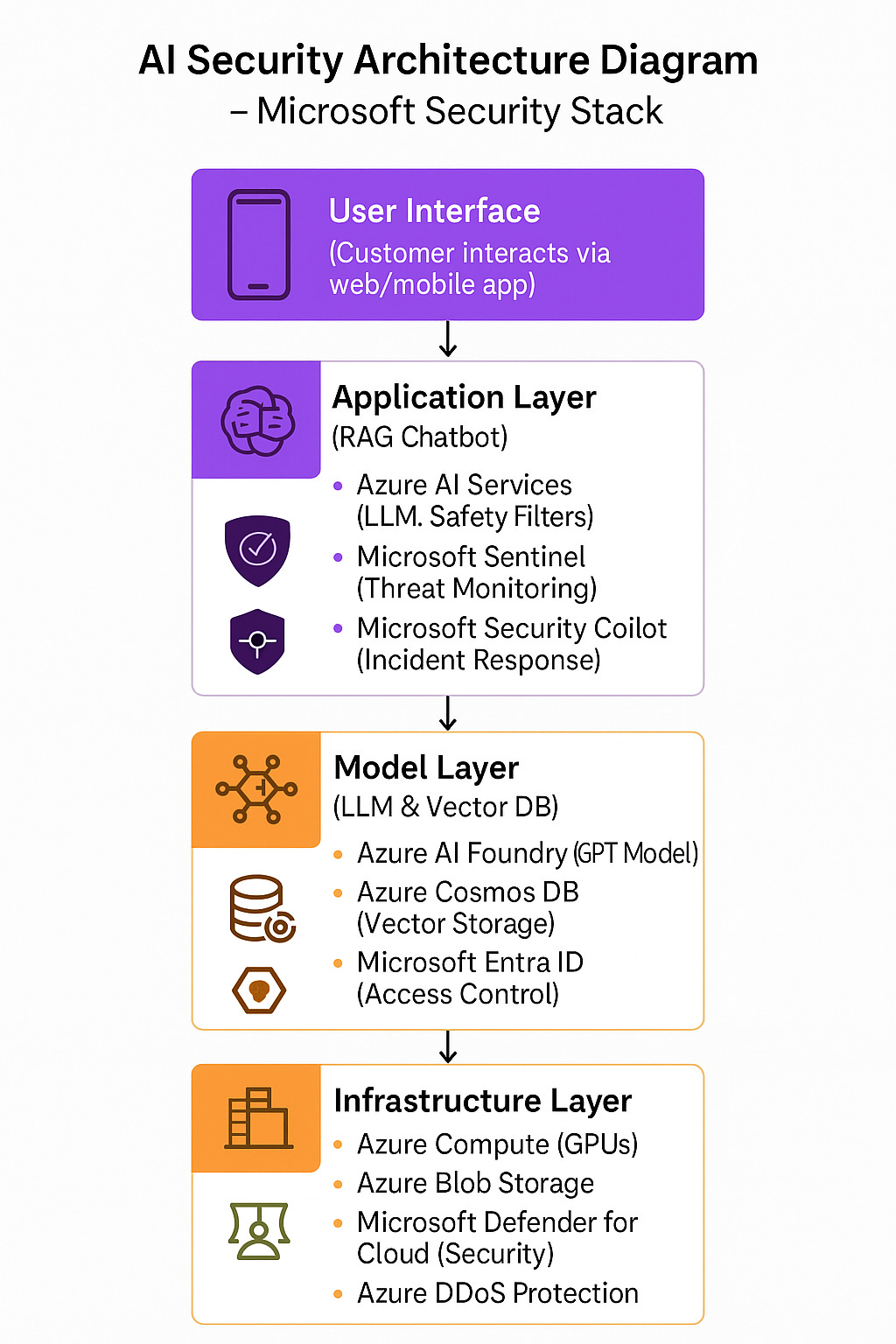
Architectural Diagram
Below is a simplified architectural diagram illustrating the integration of the Microsoft Security Stack with a RAG-based AI application.
Diagram Explanation
User Interface: Customers interact with the chatbot via a web or mobile app.
Application Layer: Azure AI Services process queries, with safety filters blocking harmful inputs/outputs. Microsoft Sentinel monitors for threats, and Security Copilot automates responses.
Model Layer: The LLM (hosted on Azure AI Foundry) retrieves data from a vector database (e.g., Azure Cosmos DB). Microsoft Entra ID secures API access.
Infrastructure Layer: Azure compute and storage are protected by Defender for Cloud and DDoS Protection.
Governance Layer: Ensures ethical AI use and compliance with regulations.
Best Practices for AI Security with Microsoft
Adopt Zero Trust: Use Microsoft Entra ID to enforce least-privilege access and verify every request.
Implement Defense-in-Depth: Apply security controls at each layer of the AI stack, from infrastructure to application.
Monitor Continuously: Leverage Microsoft Sentinel for real-time threat detection and anomaly identification.
Filter Inputs/Outputs: Use Azure AI’s safety systems to block malicious prompts and sensitive data leaks.
Ensure Compliance: Align with the Microsoft Responsible AI Standard to meet regulatory requirements and ethical guidelines.
Conclusion
The Microsoft Security Stack offers a robust framework for securing AI applications, addressing threats like prompt injections, adversarial attacks, and data breaches. By integrating tools like Microsoft Defender for Cloud, Microsoft Sentinel, and Microsoft Entra ID, organizations can protect their AI workloads while ensuring compliance and ethical use. The RAG chatbot use case demonstrates how these tools work together to deliver a secure, scalable, and efficient AI solution. As AI adoption grows, leveraging the Microsoft Security Stack will be critical to safeguarding innovation and maintaining trust.